Tibetan vs. Nepali Thangka Art: Key Differences and Meanings
Compartir
Introduction
Thangka paintings are among the most important forms of sacred Buddhist art, created across the Himalayan region for centuries. While both Tibetan and Nepali Thangkas share common roots, they also have distinct styles, techniques, and cultural influences. For collectors and practitioners, understanding these differences adds depth to the appreciation of each piece.
Historical Background
-Nepali Thangkas: The Newar artists of the Kathmandu Valley are some of the oldest Thangka painters in history. Their style influenced Tibetan Buddhism when the Dharma spread into Tibet.
-Tibetan Thangkas: Over time, Tibet developed its own unique style, blending Indian Buddhist art with native symbolism and regional aesthetics.
Key Differences Between Tibetan and Nepali Thangkas
Artistic Style
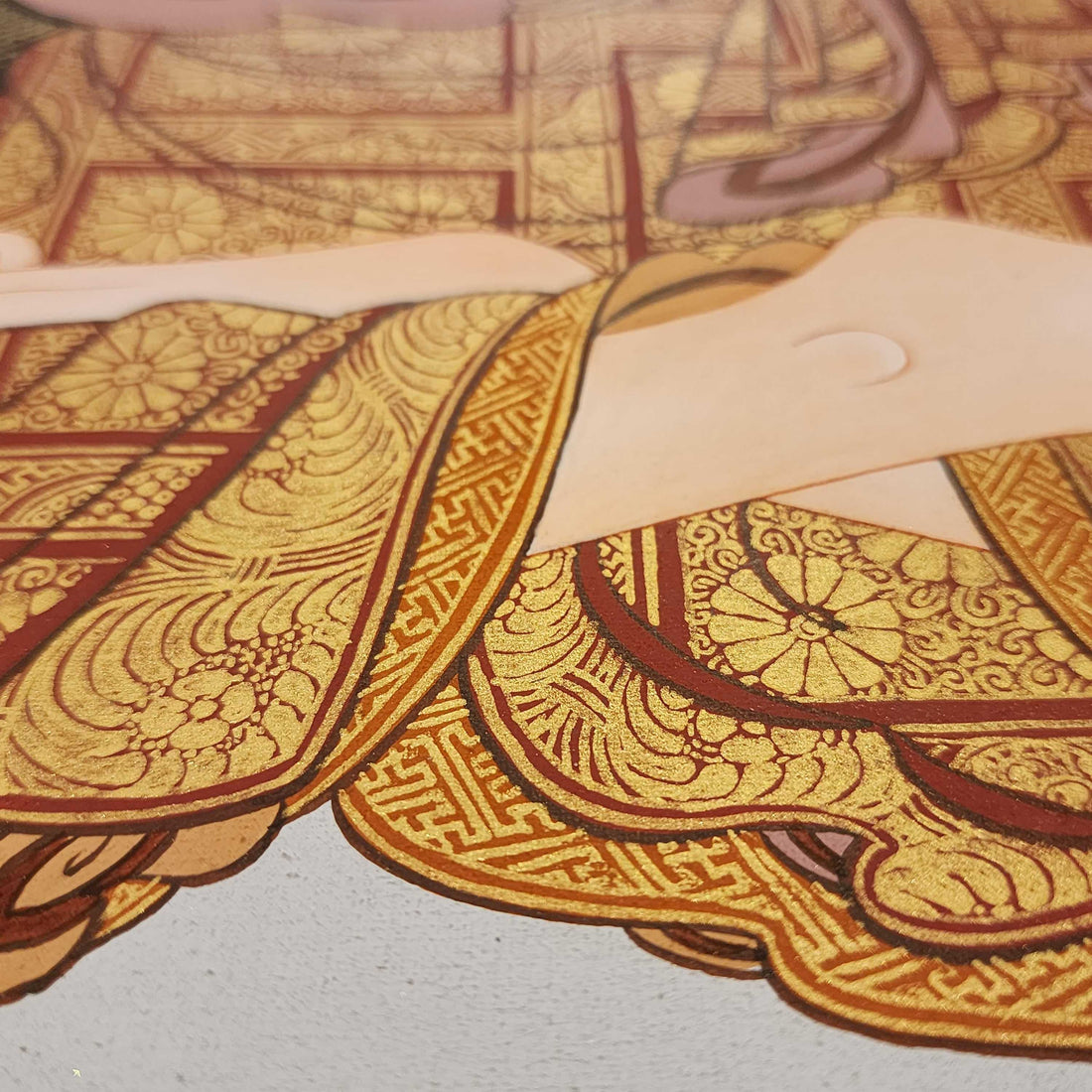
-Nepali Thangkas: Known for their fine detail, rich colors, and ornamental patterns. Figures often have rounded, expressive faces and elaborate jewelry.
-Tibetan Thangkas: More symbolic and meditative in style, with strict proportions based on scriptures. Deities may appear more stylized and less decorative.
Use of Color
-Nepali: Brighter, bolder colors with heavy use of gold.
-Tibetan: Subtler mineral pigments, sometimes muted, with emphasis on symbolic meaning.
Materials
-Nepali: Often painted on cotton with mineral pigments and 24k gold.
-Tibetan: Painted on cotton or silk, with more frequent use of brocade borders.
Themes & Subjects
-Nepali: Heavily influenced by Hinduism as well as Buddhism. You may see Hindu gods like Vishnu and Shiva alongside Buddhist figures.
-Tibetan: Primarily Buddhist subjects such as Buddhas, Bodhisattvas, mandalas, and wrathful deities.
Facial Features
-Nepali: Faces are often soft, rounded, and more human-like.
-Tibetan: Faces are stylized, symbolic, and sometimes intentionally otherworldly.
Similarities
Despite their differences, both traditions share:
-Sacred proportions guided by scripture.
-Use in meditation and rituals.
-Deep symbolic meaning beyond artistic beauty.
Which Should You Choose?
-Collectors may prefer Nepali Thangkas for their intricate, detailed style.
-Practitioners may lean toward Tibetan Thangkas for their meditative symbolism.
-Both, however, are authentic and carry spiritual value.
Conclusion
Tibetan and Nepali Thangka paintings reflect two cultural approaches to the same sacred art form. While Nepali Thangkas shine with ornate detail and vibrant beauty, Tibetan Thangkas emphasize symbolism and spiritual guidance. Together, they form a rich legacy of Himalayan Buddhist art.